How Do Bitcoin Mining and Other Cryptocurrency Mining Differ?
The main differences between Bitcoin mining and mining other cryptocurrencies can be categorized into several key areas, including consensus mechanisms, mining algorithms, transaction speeds, and overall network characteristics.
Consensus Mechanisms
- Bitcoin: Utilizes a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, where miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. This process is energy-intensive and requires significant computational power.

- Other Cryptocurrencies: While many cryptocurrencies also use PoW (like Bitcoin Cash and Litecoin), others have transitioned to Proof of Stake (PoS) or other consensus mechanisms. For instance, Ethereum has moved to PoS, which is less energy-intensive and allows users to validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold rather than computational power.
Mining Algorithms
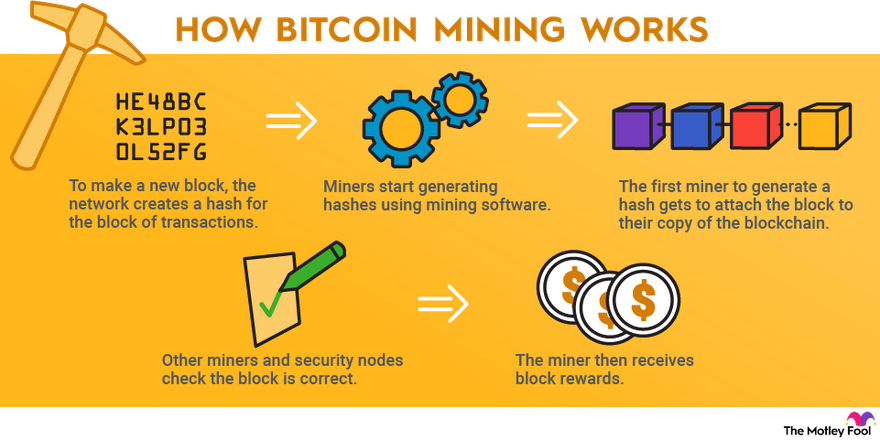
-
Bitcoin: Employs the SHA-256 hashing algorithm, which is specifically designed for Bitcoin mining. This algorithm requires specialized hardware, such as ASICs, to be competitive due to the high difficulty level of mining.
-
Other Cryptocurrencies: Different cryptocurrencies may use various hashing algorithms. For example, Ethereum Classic uses the Ethash algorithm, which is more memory-intensive and can be mined with GPUs. This diversity allows miners to choose coins based on their available hardware and energy costs.
Transaction Speeds
-
Bitcoin: Has a relatively slow transaction speed, processing about 7 transactions per second. This slower speed is partly due to its design and the time it takes to validate blocks, which occurs approximately every 10 minutes.
-
Other Cryptocurrencies: Many altcoins are designed to facilitate faster transactions. For instance, cryptocurrencies like Ripple can handle thousands of transactions per second, making them more suitable for applications requiring quick settlement times.
Network Characteristics
-
Bitcoin: As the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, it has the largest market cap and a dominant position in the market. Its mining is characterized by high competition and significant energy consumption, raising concerns about environmental impact.
-
Other Cryptocurrencies: Many altcoins have lower market caps and can be less competitive to mine. Some are designed with specific use cases in mind, such as smart contracts (Ethereum) or privacy (Monero), which can influence their mining processes and community engagement.
Conclusion
In summary, while Bitcoin mining serves as a foundational model for many cryptocurrencies, significant differences exist in terms of consensus mechanisms, mining algorithms, transaction speeds, and the overall characteristics of the networks. These differences impact the mining experience and the economic viability of participating in various cryptocurrency mining activities.
Citations:
- Koinly - Bitcoin & Crypto Mining Guide
- Freeman Law - Mining Explained: A Detailed Guide on How Cryptocurrency Mining Works
- LinkedIn Pulse - Understanding the Differences Between Bitcoin and Other Cryptocurrencies
- Kriptomat - What is Crypto Mining?
- Britannica - What is Crypto Mining?
- Investopedia - Bitcoin Mining
- Investopedia - How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
- Fidelity - What is Mining?
comments powered by Disqus