How Do Rate Cuts Affect Inflation and Employment?
How Rate Cuts Impact Inflation and Employment
When the Federal Reserve cuts interest rates, it aims to stimulate the economy and employment while keeping inflation under control. Here’s how rate cuts can impact inflation and employment:
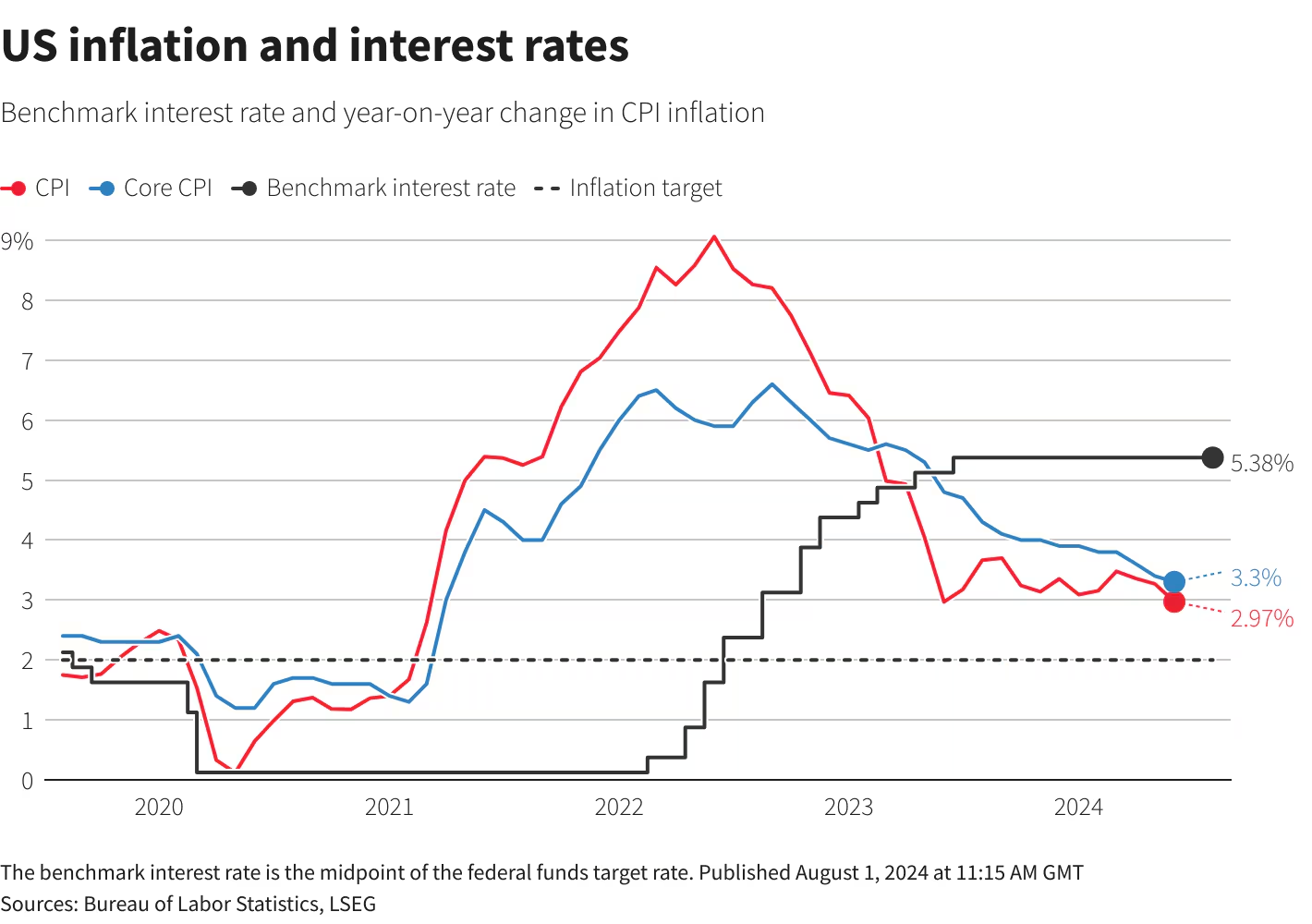
Impact on Inflation
-
Lower rates encourage spending: Cutting interest rates makes borrowing cheaper for consumers and businesses. This can spur increased spending on goods and services, creating greater demand in the economy.
-
Increased demand can push prices higher: The stronger demand for goods and services may push wages and other costs higher, putting upward pressure on inflation. However, there is often a lag between rate cuts and their effect on inflation.
-
Inflation expectations matter: If workers expect inflation to increase, they may demand higher wages, contributing to higher inflation. The Fed aims to anchor inflation expectations with its target to reduce uncertainty.
Impact on Employment
-
Cheaper borrowing can boost hiring: Lower interest rates make it cheaper for businesses to borrow money for expansion and investment. This can encourage businesses to hire more workers to meet increased demand.
-
Unemployment may fall temporarily: During recessions, the Fed may cut rates to stimulate economic growth and employment. This can lead to a temporary decline in the unemployment rate. However, once prices adjust to a new equilibrium, unemployment may rise back to the natural rate.
-
Policies to ease structural unemployment can boost jobs: While rate cuts can temporarily lower unemployment, policies aimed at reducing frictional or structural unemployment (e.g., job training programs) can boost employment without necessarily affecting inflation.
-
Tight labor markets can contribute to inflation: If there is a mismatch between labor demand and supply, companies may boost wages to recruit more workers. However, research suggests higher wages have only contributed modestly to recent inflation.
In summary, the Fed cuts rates to stimulate the economy and employment, but this can also lead to higher inflation if rates are kept too low for too long. The central bank must carefully balance the risks between controlling inflation and maintaining full employment.
References
- Federal Reserve - What is the Federal Reserve?
- Darden School of Business - What a Fed Rate Cut Could Mean for Your Wallet
- Investopedia - How Inflation and Unemployment Are Related
- Bankrate - How Federal Reserve Impacts Your Money
- Bolton USA - Understanding Fed Rate Cut
- IMF - Unemployment
- RBA - The Transmission of Monetary Policy
- Investopedia - Inflation and Interest Rate Relationship
comments powered by Disqus