What is Cryptocurrency and How Does It Work?
Cryptocurrency refers to a form of digital or virtual currency that utilizes cryptography for security, making it nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend. Unlike traditional currencies, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks based on blockchain technology, which is a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. This decentralized nature means that cryptocurrencies are not issued or regulated by any central authority, such as a government or financial institution, allowing for peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries.
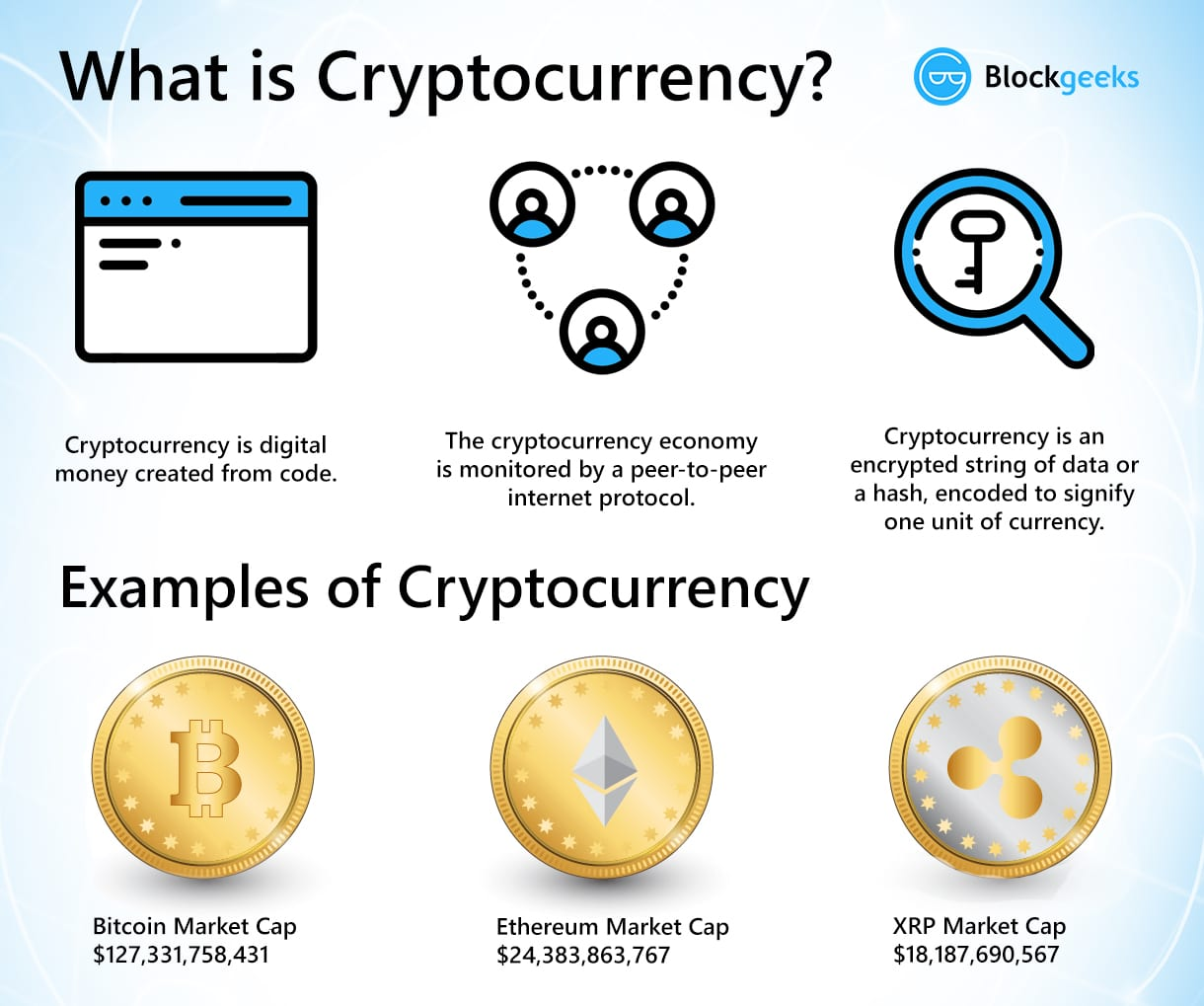
Key Characteristics of Cryptocurrency
-
Digital Nature: Cryptocurrencies exist solely in digital form and do not have a physical counterpart like coins or banknotes.
-
Decentralization: They are maintained through a network of computers (nodes) that validate and record transactions on a public ledger, ensuring transparency and security.
-
Cryptographic Security: Transactions are secured using cryptographic techniques, which help prevent fraud and ensure the integrity of the currency.
-
Variety of Types: The most well-known cryptocurrency is Bitcoin, created in 2009, but there are thousands of others, including Ethereum, Litecoin, and Ripple, each with unique features and purposes.
Functionality
Cryptocurrencies can be used for various purposes, including online purchases, investment, and as a means of transferring value across borders quickly and with lower fees compared to traditional banking systems. They are stored in digital wallets and can be traded on various platforms.
In summary, cryptocurrency represents a significant shift in how we think about money and transactions, leveraging technology to create a new form of currency that operates independently of traditional financial systems.
Citations:
comments powered by Disqus