What's the Difference Between PT and OT?
Physical Therapy (PT) and Occupational Therapy (OT) are both essential forms of rehabilitative care, but they serve different purposes and focus on distinct aspects of recovery and rehabilitation.
Focus and Goals
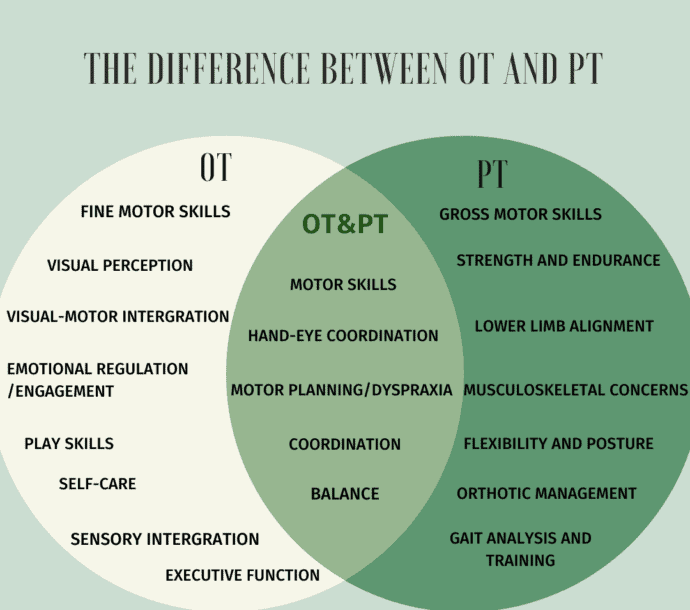
Physical Therapy (PT)
-
Primary Goal: PT primarily focuses on improving movement, strength, and range of motion. It aims to alleviate pain, restore physical function, and enhance mobility after injuries or surgeries.
-
Methods: Physical therapists employ exercises, stretches, manual therapy, and modalities like heat or electrical stimulation to help patients regain physical capabilities. For instance, a patient recovering from knee surgery would work with a PT to strengthen the knee and improve its range of motion.
Occupational Therapy (OT)
-
Primary Goal: OT is centered around helping individuals perform daily activities more independently. This includes enhancing fine and gross motor skills necessary for tasks such as dressing, eating, or managing household chores.
-
Methods: Occupational therapists assess the patient’s environment and daily routines, often making modifications to facilitate independence. They may also provide adaptive tools or strategies to help clients overcome challenges related to cognitive or physical impairments.
Scope of Practice
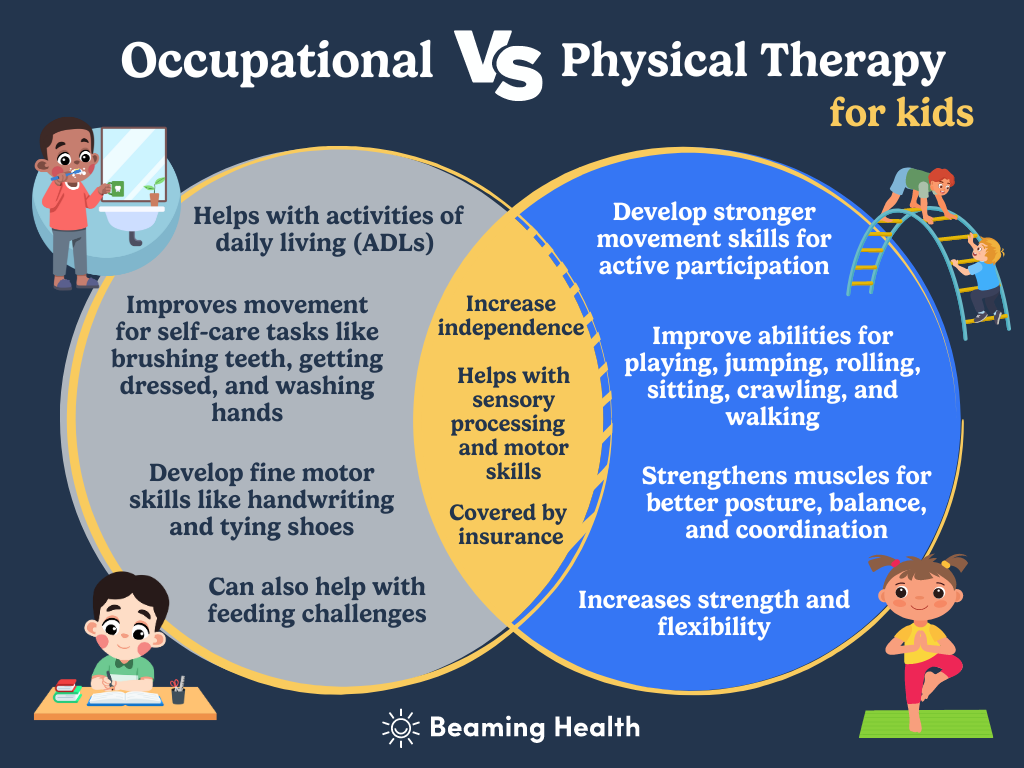
-
PT: Physical therapists typically address biomechanical issues related to movement. They work with patients recovering from musculoskeletal injuries or surgeries, focusing on physical rehabilitation.
-
OT: Occupational therapists take a more holistic approach that encompasses not just the physical aspects but also emotional and social factors. They assist patients in adapting their environments and routines to improve overall quality of life.
Overlap and Collaboration
While PT and OT have distinct focuses, there is significant overlap in their practices. Both types of therapists may work together in multidisciplinary teams to provide comprehensive care for patients recovering from conditions like strokes or surgeries. For example, while a PT might focus on improving a patient’s balance and strength, an OT might assist the same patient in relearning how to perform daily tasks like grooming.
Conclusion
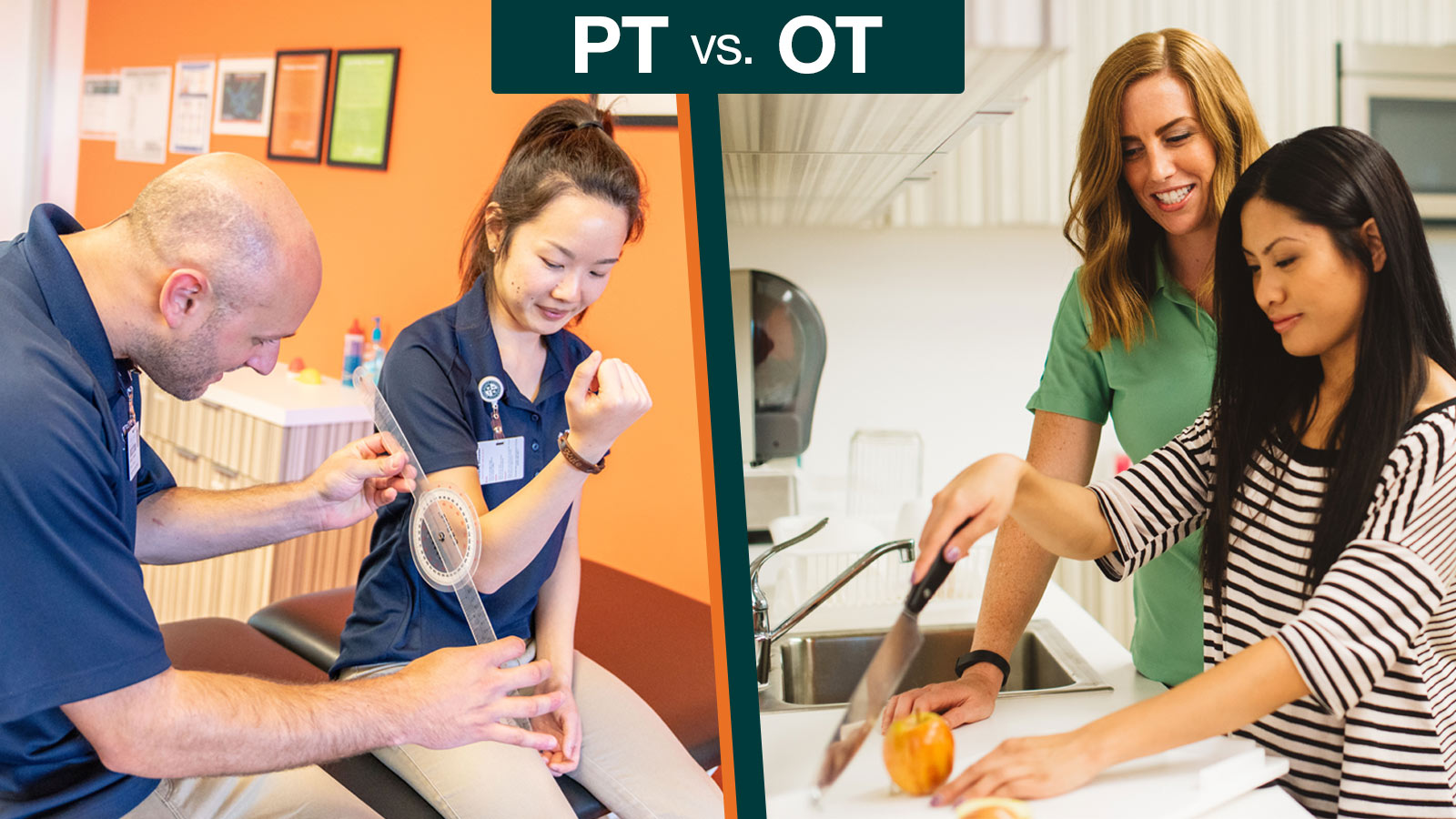

In summary, the key difference between PT and OT lies in their primary objectives: PT aims to restore physical function and reduce pain through movement-based interventions, while OT focuses on enhancing daily living skills and promoting independence through a broader approach that includes environmental adaptations and skill development. The choice between the two therapies depends on individual needs and specific rehabilitation goals.
References
- Healthline - Occupational Therapy vs. Physical Therapy
- Creighton University - Occupational Therapist vs. Physical Therapist
- OTA Online - Occupational Therapy vs. Physical Therapy
- USA University - Physical Therapy vs. Occupational Therapy
- Access Physical Therapy & Wellness - What is the Difference Between OT and PT?
- Regis College - Occupational Therapy vs. Physical Therapy: Key Differences
- Joyce University - Occupational Therapy vs. Physical Therapy
- WebMD - Occupational Therapy Versus Physical Therapy
comments powered by Disqus